Compassionate Gynaecological Care, Expertly Tailored for Every Woman

High-risk pregnancy management and fetal surgery provide essential services to women who have medical complications or fetuses with certain medical conditions. A high-risk pregnancy is one where the mother or baby has an increased risk of health problems. This can include conditions like gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, advanced maternal age, multiple pregnancies (twins or triplets), or prior miscarriage. Management is initiated with full monitoring, advanced imaging, and a specific treatment strategy. In some cases, fetal surgery may be needed to treat certain conditions, such as spina bifida, twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome or congenital diaphragmatic hernia, while the baby is still in the uterus. Ideal candidates for high-risk pregnancy care are women who have abnormal ultrasound reports along with pre-existing health problems. Multidisciplinary teamwork involving obstetricians, neonatologists, genetic counsellors and fetal medicine experts is of pivotal importance. These are interventions to maximise maternal health and avoid preterm birth. Despite being technically difficult, a fetal surgery can greatly minimise, or in some cases save, lifelong issues for the unborn child. With careful monitoring and state-of-the-art medical procedures, many high-risk pregnancies lead to successful deliveries of healthy babies.

Robotic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgery used to perform a hysterectomy through tiny incisions using a robotic device. It is usually recommended in conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding or cancer. Tiny incisions are made in the abdomen. After that, a 3D camera and robotic arms are inserted during the surgery. Surgeons, working from a console, manoeuvre the robotic arms to precisely cut the uterus with little to no damage to nearby tissues. This method provides more accuracy and fewer complications. Ideal patients include women who need a hysterectomy but prefer a less invasive method that allows them to resume normal activities sooner. Robotic surgery is especially beneficial for those with complex anatomy or extensive adhesions. Compared to traditional open surgery, robotic hysterectomy results in less pain, minimal blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and smaller scars. It also allows for better preservation of nearby organs and nerves. Most patients recover fully within two weeks. This procedure empowers women with a safe and effective surgical option that balances medical need with faster healing and improved quality of life.

Surgical treatment for endometriosis and uterine fibroids is often required when symptoms become severe or unresponsive to medication. These conditions can cause pelvic pain, heavy periods, infertility, and significant discomfort in day-to-day life. Endometriosis surgery involves the removal or destruction of endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus. Fibroid surgery, or myomectomy, removes noncancerous growths from the uterus. Both procedures can be performed using laparoscopic or robotic-assisted techniques, minimising incisions and speeding up recovery. Women experiencing painful menstruation, pelvic pressure, abnormal bleeding, or difficulty conceiving are ideal candidates. Minimally invasive surgery is especially suited for women who want to preserve their uterus for future pregnancy. These procedures restore uterine health, relieve symptoms, and improve reproductive outcomes. For many women, surgical intervention means a drastic improvement in quality of life, physically, emotionally, and sexually. Recovery typically takes 1–2 weeks, with patients returning to normal activities much faster than with traditional open surgery. With advanced surgical tools and highly skilled specialists, treating fibroids and endometriosis no longer has to be invasive or life-disrupting; it can be transformative and liberating.
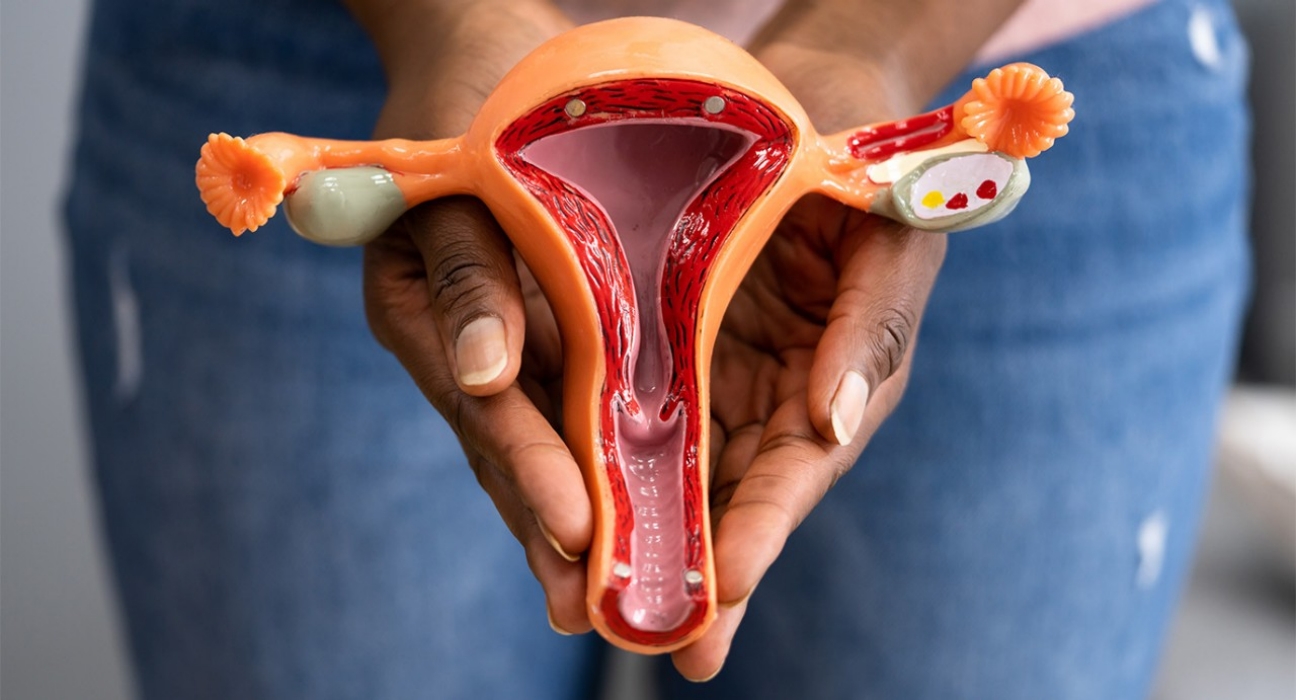
Ovarian cancer surgery is a crucial step in diagnosing and treating this often-silent yet aggressive disease. The goal of the procedure is to remove as much cancerous tissue as possible to improve survival rates and reduce the need for extensive chemotherapy. Surgical approaches vary depending on the stage and type of cancer. Debulking surgery is common in advanced cases and involves removing the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, surrounding lymph nodes, and any visible tumours in the abdominal cavity. In early-stage cancer, unilateral or bilateral oophorectomy may be sufficient. The surgery may be performed via open or minimally invasive methods based on the extent of the disease. Ideal candidates include women diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer or those with suspected malignancies from imaging and blood tests like CA-125. It may also be done preventively in women with genetic risks like BRCA mutations. This procedure not only helps in cancer control but also provides definitive staging, which is essential for follow-up treatment decisions. Early intervention through surgery can significantly enhance prognosis and provide a chance for long-term remission. Ovarian cancer surgery remains a cornerstone of gynecologic oncology, offering women renewed hope through timely and expert surgical care.
Hospital
Kenganar Multispeciality Hospital
Obstetrics & Gynecology (OBG)
#3,28/03 ,Chikkagollarahatti, Kochahalli Gate,Magadi Main Road.
- Bangalore, Karnataka
-
Timings:
24/7 Service
Oncology International India
Obstetrics & Gynecology (OBG)
741, Outer Ring Rd, KR Layout, JP Nagar Phase 6, J. P. Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560078
- Bangalore, Karnataka
-
Timings:
24/7 Service



















